Cart (0 Items)
Your cart is currently empty.
View Products


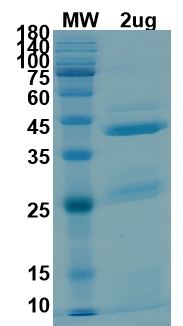
| size | 100ug, 50ug |
|---|---|
| Brand | ProteoGenix |
| Product type | COVID-19 products |
| Host Species | Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Product name | NSP15 |
|---|---|
| Origin species | SARS-COV2 |
| Expression system | Prokaryotic expression |
| Molecular weight | 41,2kDa |
| Purity estimated | 80% |
| Buffer | PBS, pH7.5, 0.02%NLS |
| Form | liquid |
| Delivery condition | Dry Ice |
| Storage condition | 4°C for short term; -20°c or -80°C for long term |
| Brand | ProteoGenix |
| Host species | Escherichia coli (E.coli) |
| Fragment Type | Full length |
| Aliases /Synonyms | Nidoviral RNA uridylate-specific endoribonuclease |
| Reference | PX-COV-P030 |
| Note | For research use only |
SARS-CoV-2 non-structural protein 15 (nsp15) is one of 16 proteins found in the genome of the new strain of coronavirus. Nsp15 is a nidoviral RNA uridylate-specific endoribonuclease (NendoU) with a C-terminal catalytic domain from the EndoU family. This family of endonucleases is known to cleave either single-stranded or double-stranded RNA producing 2’-3’ cyclic phosphodiester and 5’-hydroxyl termini. The nps15 protein was found to be highly conserved among coronaviruses. Particularly within the catalytic domain found in the three zoonotic coronaviruses: SARS-CoV, MERS-CoV, and SARS-CoV-2. However, experts argue that despite the high levels of similarity, differences at the sequence level may contribute to the increased virulence associated with the COVID-19 disease.
Recent studies suggest that nsp15 may interfere with the innate immune response, while its role in replication and other viral processes remains elusive. The 39 kDa monomeric unit of nsp15 was found to form hexamers and to fold into three domains: N-terminal, middle domain, and the catalytic C-terminal domain. Its active site was shown to be Mn2+-dependent and specific towards uridylate found in unpaired regions.
Prior studies show that coronavirus can infect macrophages and delay the innate immune response. This process seems to be crucial for pathogenesis in coronavirus, since disabling the stability and activity of nsp15 resulted in attenuated infections. Studies suggest that nsp15 may act as an antagonist of dsRNA sensors in macrophages. Moreover, this protein is associated with viral replication complexes suggesting that it may sequester viral dsRNA within these complexes and keep then “hidden” from the host dsRNA sensors. However, the exact process through which the protein’s endoribonuclease activity interferes with the host immune system is still poorly understood.
Unlike other proteins found in SARS-CoV-2, nsp15 has a poorly characterized function. For this reason, nsp15 may serve only as a complementary target for drug or vaccine development. By blocking the virus’ ability to elude the innate immune system, it might be possible to further engage the host’s immune system during the early stages of infection.

Send us a message from the form below
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.