Cart (0 Items)
Your cart is currently empty.
View Products


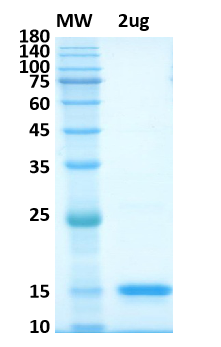
| size | 100ug, 50ug |
|---|---|
| Brand | ProteoGenix |
| Product type | COVID-19 products |
| Host Species | Escherichia coli (E. coli) |
| Product name | NSP9 |
|---|---|
| Origin species | SARS-COV2 |
| Expression system | Prokaryotic expression |
| Sequence | YP_009725305.1 |
| Molecular weight | 12,3kDa |
| Purity estimated | 90% |
| Buffer | PBS, pH7,5 |
| Form | liquid |
| Delivery condition | Dry Ice |
| Storage condition | 4°C for short term; -20°c or -80°C for long term |
| Brand | ProteoGenix |
| Host species | Escherichia coli (E.coli) |
| Fragment Type | Full length |
| Reference | PX-COV-P018 |
| Note | For research use only |
Nonstructural protein 9 (nsp9) is an essential RNA binding protein found in coronavirus (CoV). CoV affects humans and animals and can cause widespread respiratory, central nervous system and gastrointestinal diseases. Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) , a CoV species, is responsible for corona virus disease 2019 (COVID-19). CoVs are enveloped viruses, with positive single-stranded RNA genomes of 30 kb in length. CoV genome encodes open reading frame (ORF) 1a and ORF 1ab polyproteins. These two polyproteins are then processed to form 16 nonstructural proteins. These proteins are involved in transcription, replication and translation of viral genome. Nsp9 protein, along with nsp7, nsp8 and nsp10, is located within the replication complex. Nsp9 interreacts with nsp8 protein for its functions. Nsp9 impairment leads to defective viral RNA synthesis. The dimerization of nsp9 protein is believed to be essential for viral replication to occur. SARS-CoV nsp9 protein has RNA/DNA binding activity. However, it has been shown that the interaction between nsp9 and single stranded nucleic acid binding protein (ssDNA and ssRNA) was weak and non-specific.
CoV nsp9 displays an oligosaccharide/oligonucleotide fold-like fold. The protein consists of monomers that contain seven antiparallel ß -strands, one α-helix appended at the C terminus of the polypeptide chain and loops that connect the strands. Nsp9 protein forms a homodimer which binds single‐stranded RNA. The dimer is formed through the interaction protein-protein interaction motif GXXXG located in parallel α-helices. The disulfide bonds are considered to be essential for nsp9 dimerization. The dimerization is believed to be formed between N-fingers and the the C-terminal α -helice and N-finger. Further stabilization is derived from the close packing of the helices from the two monomers. 6-stranded ß-barrels are thought to build up the core of the protein. The barrels consists of two antiparallel ß-sheets packed orthogonally. Nsp9 is homologues to serine proteases particularly the second domain of 3CL protein found in coronavirus.

Send us a message from the form below
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.