Cart (0 Items)
Your cart is currently empty.
View Products



| size | 100ug, 50ug |
|---|---|
| Brand | ProteoGenix |
| Product type | COVID-19 products |
| Host Species | Mammalian cells |
| Product name | RBD Domain |
|---|---|
| Origin species | SARS-COV2 |
| Expression system | Eukaryotic expression |
| Sequence | MN908947 |
| Molecular weight | 23,6kDa |
| Purity estimated | 95% |
| Buffer | PBS, pH 7,5 |
| Form | Liquid |
| Delivery condition | Dry Ice |
| Storage condition | 4°C for short term; -20°c or -80°C for long term |
| Brand | ProteoGenix |
| Host species | Mammalian cells |
| Fragment Type | Spike protein fragment |
| Aliases /Synonyms | Receptor binding domain (RBD) in Spike protein S1 |
| Reference | PX-COV-P046 |
| Note | For research use only. Not suitable for human use. |
RBD is a receptor-binding domain located on the spike protein of coronavirus (CoV). The Severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) is responsible for coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a CoV species. COVID virus contains four structural proteins; spike (S), nucleocapsid (N), envelope (E) and membrane (M) proteins. CoV spike protein is responsible for viral attachment, fusion and entry. Spike protein consists of two domains, namely S1 and S2, which are responsible for the binding step. S1 domain is involved in host cell receptor recognition and binding whereas S1 domain contain the putative fusion peptide as well as heptad repeat HR1 and HR2. S1 contains RBD protein domain.
RBD domain is believed to have a pivotal role in spike protein-induced viral attachment, fusion and entry. RBD domain binds strongly to angiotensin-converting enzyme 2 (ACE2) receptors. These receptors are located in the cells of most organs including lungs, kidneys, heart, arteries and cerebral cortex. Once the spike protein binds to ACE2 receptors, the viral enters the cell via endocytosis and is soon after transferred in the endosome of the target cell. SARS-CoV-2 RBD shows high binding affinity to ACE2 receptors with human and bat origin. SARS-CoV-2 RBD binds strongly to 293T-expressed in bat cell ACE2 receptors with a similar intensity to that of its binding to 293T-expressed in human cell ACE2 receptors. Furthermore, the binding is dose dependent. The strong binding of SARS-CoV RBD to either bat ACE2 or human ACE2 may partially explain why SARS-CoV-2 is more transmissible than other CoV species.
Polyclonal antibodies that specifically targeted RBD domain of SARS-CoV spike protein and cross-reacted with SARS-CoV-2 RBD protein were able to inhibit SARS-CoV-2 entry into target human cells that expressed ACE2 receptor. Furthermore, polyclonal antibodies cross-neutralized SARS-CoV-2 pseudovirus infection. This suggest a SARS-CoV RBD-based vaccine as a potential target for prevention of infection by SARS-CoV-2 and SARS-CoV.


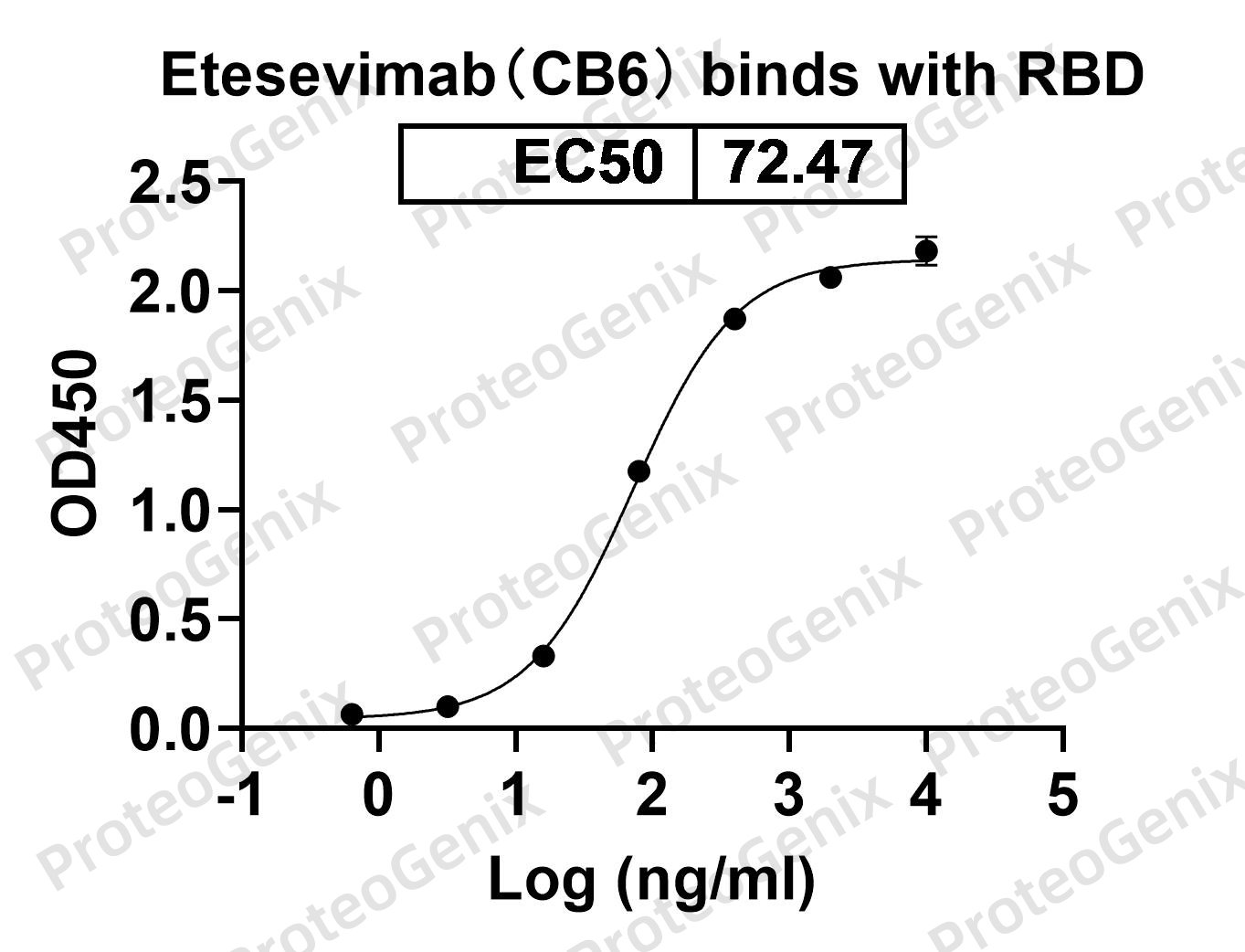
Immobilized RBD Domain (cat. No.PX-COV-P046) at 0.5µg/mL (100µL/well) can bind to Anti-RBD-1 (Etesevimab) antibody (cat. No.PTXCOV-A549) in indirect ELISA with Goat Anti-Human IgG secondary antibody coupled with HRP measured by OD450
Related products
Send us a message from the form below
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.