Cart (0 Items)
Your cart is currently empty.
View Products


| Size | 100ug, 50ug |
|---|---|
| Brand | ProteoGenix |
| Product type | COVID-19 products |
| Host Species | Mammalian cells |
| Product name | SARS-CoV-2 RBD of Spike protein, S477N – lineage B.1.526 – NY Iota Variant |
|---|---|
| Origin species | SARS-COV2 |
| Expression system | Eukaryotic expression |
| Sequence | YP_009724390.1 |
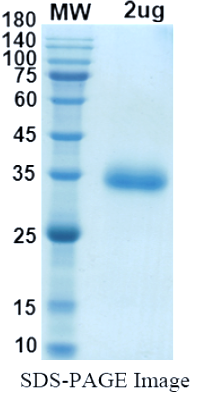
| Molecular weight | 35kDa |
| Buffer | PBS, pH7.5 |
| Delivery condition | Dry Ice |
| Storage condition | 4°C for short term; -20°c or -80°C for long term |
| Brand | ProteoGenix |
| Host species | Mammalian cells |
| Applications | ELISA,WB |
| Fragment Type | Spike protein fragment |
| Aliases /Synonyms | lineage B.1.526, New Yorker variant, Nyvariant, Iota variant |
| Reference | PX-COV-P058 |
| Note | For research use only. Not suitable for in vitro diagnostic and human use. |
During the last quarter of 2020, investigators have witnessed the rise of several variants carrying multiple mutations with biological significance. Many of these biologically relevant mutations are focused on the receptor-binding domain (RBD) of the spike protein of SARS-CoV-2. Residues that are responsible for binding the human receptor ACE2 or those that are bound by neutralizing antibodies are the ones suffering the most changes.
In November 2020, a new lineage of SARS-CoV-2 was detected in the state of New York (USA) by researchers from Caltech and Columbia University. The most common set of mutations found in the spike protein of the new lineage – B.1.526 – are L5F, T95I, D253G, E484K or S477N (never the two at the same time), D614G, and A701V. The relative abundance of this lineage in the NY area has reached 25% in February 2021, representing a 26-fold increase in a little over a month. Its frequency is expected to keep rising in the months to come.
Mutation E484K is shared with lineages B.1.351 (South Africa) and P.1 (Brazil) and suspected to increase SARS-CoV-2’s ability to evade the immune system by reducing the potency of class 1 antibodies that target this region. Mutation S477N has also been detected in other lineages of SARS-CoV-2, but this is the first time a lineage carrying it becomes so abundance in the circulating SARS-CoV-2 population. This mutation may be associated with an increased affinity towards the human ACE2 receptor and increased resistance to SARS-CoV-2 neutralizing antibodies.
The fact that this is the first time we are seeing a steady increase of viruses carrying the S477N mutation can be explained by its association with the D253G, adjacent to the RBD. This mutation falls into the loop of the N-terminal domain (NTD) of the spike. For this reason, it is expected to abolish an important neutralizing epitope in this region and contribute to increased immune resistance. The combination of E484K or S477N with D253G may exacerbate SARS-CoV-2 infectivity and contribute to a new surge of COVID-19 cases worldwide.
This RBD fragment contains the S477N mutation found in lineage B.1.526. For the variant carrying the E484K mutation, click here.

Related products
Send us a message from the form below
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.