Cart (0 Items)
Your cart is currently empty.
View Products


| size | 100ug, 50ug |
|---|---|
| Brand | ProteoGenix |
| Product type | COVID-19 products |
| Host Species | Mammalian cells |
| Product name | SARS-CoV-2 RBD of Spike protein, L452R, T478K – lineage B.1.617.2 – Indian Delta Variant |
|---|---|
| Origin species | SARS-COV2 |
| Expression system | Eukaryotic expression |
| Sequence | YP_009724390.1 |
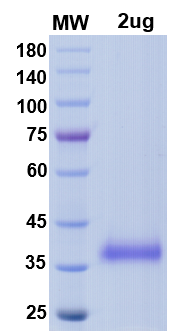
| Molecular weight | 35kDa |
| Buffer | PBS, pH7.5 |
| Form | Liquid |
| Delivery condition | Dry Ice |
| Storage condition | 4°C for short term; -20°c or -80°C for long term |
| Brand | ProteoGenix |
| Host species | Mammalian cells |
| Fragment Type | Spike protein fragment |
| Aliases /Synonyms | B.1.617.2, VOC21APR-02, G/452R.V3, Indian variant, Delta variant |
| Reference | PX-COV-P061 |
| Note | For research use only. Not suitable for human use. |
There are currently three circulating clades of lineage B.1.617 – B.1.617.1, B.1.617.2, and B.1.617.3, shown in chronological order of detection. Although these clades display different mutation profiles, all were initially detected in India and have since spread to other continents. Of the three clades, lineage B.1.617.2 carrying receptor-binding domain mutations L452R and T478K is the one causing more concern among the scientific community and governments.
Public Health England (PHE) has recently escalated lineage B.1.617.2 from variant under investigation (VUI) to variant of concern – VOC21APR-02 – due to the steep increase of cases in the UK. In early May 2021, the number of cases of this variant with a travel history in India already represented a minority of the total amount of B.1617.2 cases detected in the country. Data suggests a sustained spread of the new variant and hints to its higher infectivity in comparison to other circulating variants of SARS-CoV-2. Although the absolute number of cases remains low, the spread rate of this variant is very high. These findings suggest variant B.1.617.2 may possess transmissibility similar to that of B.1.1.7, one of the most abundant variants of the virus circulating in the UK since September 2020. But it is still unclear if this variant will outcompete the UK strain.
Mutation L452R has been previously detected in two other high abundance variants circulating in the US (lineages B.1.427 and B.1.429). This mutation has been associated with weaker neutralization of the virus by convalescent plasma. However, the available data is still insufficient to understand how this amino acid change might affect vaccine efficiency. Less data is available on the effects of mutation T478K. This amino acid change occurs in the region of interaction between the virus and the human ACE2 receptor. Several lineages of SARS-CoV-2 have been shown to carry this mutation, namely lineage B.1.1.519 (US/Mexico lineage). Moreover, several reports indicate that its abundance among circulating variants has shown a marked increase since January 2021. To date, there are no reports regarding the effects of this change on the transmissibility and immune evasion ability of SARS-CoV-2. For this reason, more functional studies are necessary to determine the potential effect of these combined RBD mutations on COVID-19 vaccine and drug efficiency.

Related products
Send us a message from the form below
Reviews
There are no reviews yet.